6 Common Mosquito Types
There are more than 3,000 mosquito species1 buzzing around virtually every corner of the planet. Get the facts about some of the most common mosquito types—and find out how to fight them.
Powered by the SC Johnson Center for Insect Science®
We’ve spent 60 years studying mosquitoes—from what attracts mosquitoes to how they transmit diseases. At the SC Johnson Center for Insect Science™, our experts raise and study thousands of these blood-sucking insects on any given day. Find out what we know about six common mosquito types and learn ways to help protect your loved ones from these biting bugs.
1. Yellow fever mosquito
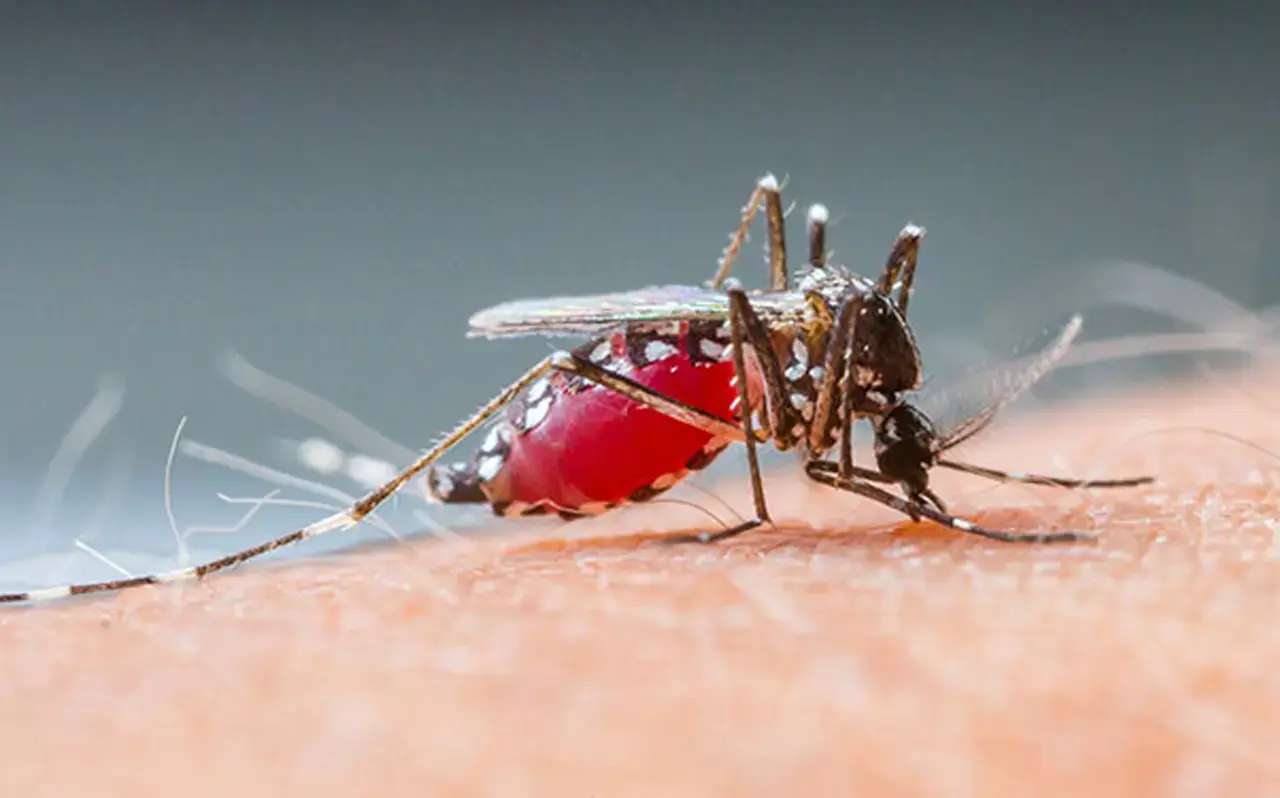

While the Aedes aegypti is commonly known as the yellow fever mosquito, this blood-hungry pest may also transmit dengue, chikungunya virus, and Zika.2 The Aedes aegyptimostly bites during the daytime and typically lives in urban areas in tropical and subtropical regions. This mosquito species prefers to bite humans and is commonly found indoors.
2. Asian tiger mosquito

The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is known to spread dengue, chikungunya, and dirofilariasis.3 The species originated in Asia, but this world-traveling insect is now also found in North America, South America, Europe, Africa, and islands in the Pacific and Indian oceans. Unlike the yellow fever mosquito, the Asian tiger mosquito can survive in colder climates.
3. Anopheles mosquito
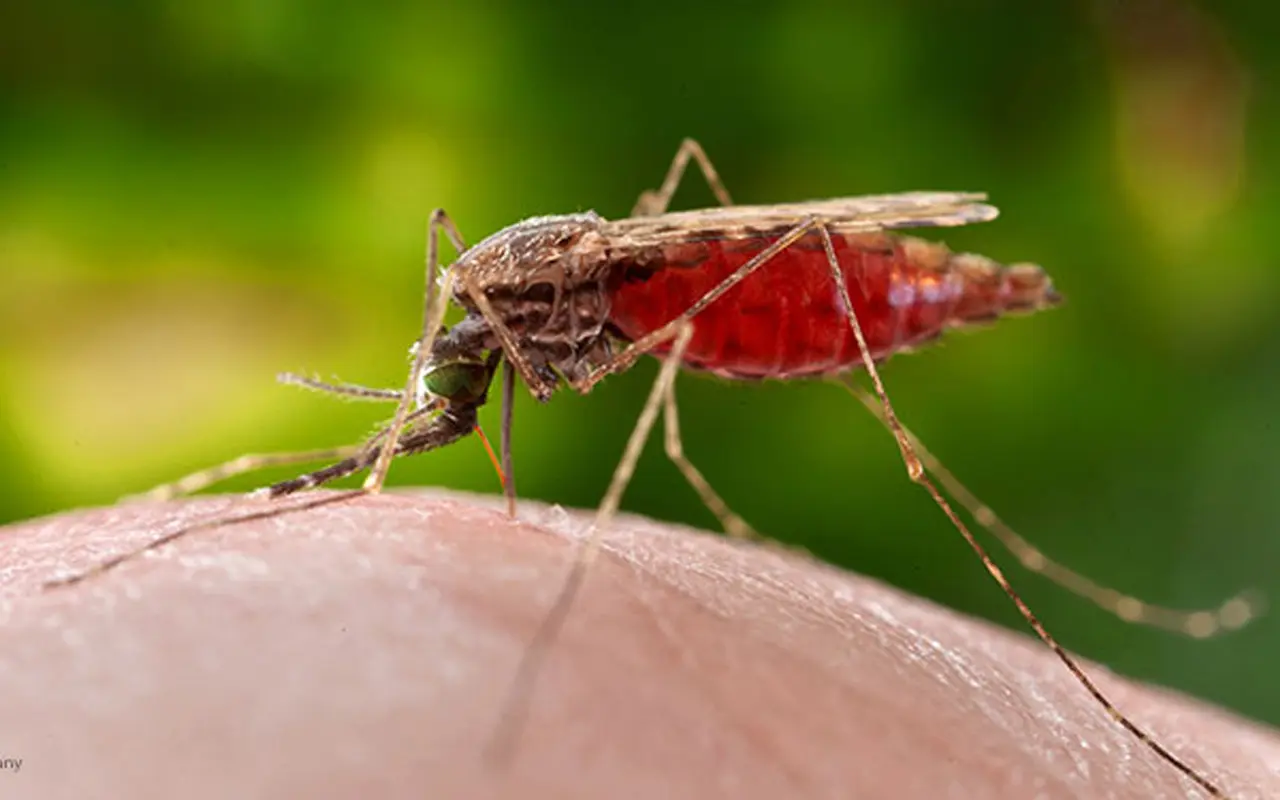

Anopheles mosquitoes lays eggs with built-in floatation devices. Like all mosquitoes,Anopheleseggs develop in the water, but the eggs of this genera are uniquely equipped with floats on either side. Females generally lay 50-200 eggs at a time that take about two to three days to hatch. The Anopheles gambiaemosquito transmits malaria and bites mostly at night.
Only female mosquitoes bite
Both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and plant sap, but only female mosquitoes bite because they need blood to nourish their eggs. During a single meal, a female mosquito can drink her entire body weight in blood.4 Learn how to treat mosquito bites and help ditch the itch.
4. Southern house mosquito
The southern house mosquito goes by the scientific name Culex quinquefasciatus.The species feasts on birds, people, and other mammals. Southern house mosquitoes make their home in tropical and subtropical regions of the world and are known to transmit West Nile virus.5
5. Pitcher plant mosquito
Mosquito moms look for a watery environment for their eggs to develop in. The pitcher plant mosquito (Wyeomyia smithii) seeks out certain small pools for their eggs, like the ones found inside leaves of the carnivorous purple pitcher plant. Adult mosquitoes lay their eggs and fly away to safety, but other insects aren’t so lucky. Ants, moths, and flies that fall into the pitchers can drown and end up as food for developing mosquito larvae. Once the bugs are digested, the larvae excrete the essential nutrients the bugs provide in their feces. The pitcher plant then absorbs the nutrients.6
The pitcher plant mosquito is unique because it is the only species that has some female mosquitoes that bite and others that don’t. Researchers are studying these mosquitoes to see if there is a way to turn off the biting gene in other species, which could help eliminate mosquito-borne diseases worldwide.7
6. Eastern saltmarsh mosquito
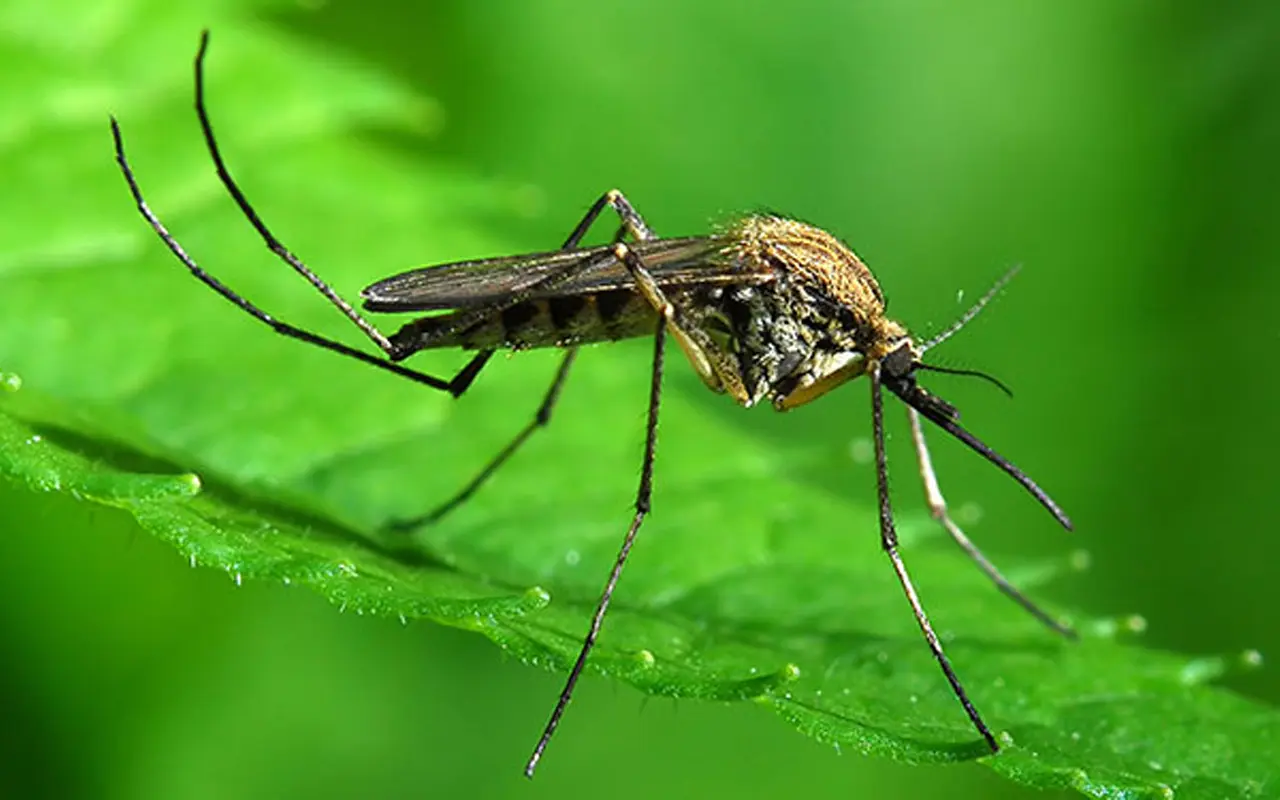

Eastern saltmarsh mosquitoes are found primarily along the Atlantic coast from northeastern Canada south to Florida and down the Gulf of Mexico to Texas.8 However, the eastern saltmarsh mosquito isn’t afraid to travel. While most mosquitoes stay close to their breeding grounds, this species will leave the salt marshes they hatch in and may travel as far as 40 miles looking for a blood meal. The eastern saltmarsh mosquito’s scientific name is Aedes sollicitans. In Latin, this means “vexing” or “disturbing,” which is quite appropriate as the females bite aggressively day or night and will feast on people and many kinds of animals, including birds, reptiles, and mammals.8
How to keep mosquitoes away
Now that you know some of the common mosquito types around the world and the diseases they spread, find out how to help protect your family and fight these pesky pests.
Find solutions for mosquitoes
Browse a variety of products designed to help you get tough in the fight against mosquitoes.
Sources
- https://extension.psu.edu/mosquitoes
- https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/facts/mosquito-factsheets/aedes-aegypti
- https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/facts/mosquito-factsheets/aedes-albopictus
- https://uanews.arizona.edu/story/making-blood-sucking-deadly-for-mosquitoes
- http://entnemdept.ufl.edu/creatures/aquatic/southern_house_mosquito.htm
- https://www.nytimes.com/2018/03/07/science/pitcher-plants-insects.html
- https://news.nd.edu/news/researchers-isolate-biting-non-biting-genes-in-pitcher-plant-mosquitoes/
- http://www.vdci.net/blog/mosquito-of-the-month-april-2016-aedes-sollicitans-eastern-saltmarsh-mosquito
Related

Chikungunya: Symptoms, Treatment, & Prevention
Beyond being pesky, mosquitoes can also spread diseases like the Chikungunya virus. Learn about the symptoms of Chikungunya and how to help protect your loved ones from mosquitoes that may carry diseases.

Dengue: Virus Protection and Disease Symptoms
Dengue is a deadly virus that is caused by the bite of a mosquito infected with any one of four dengue virus serotypes. Every year, the disease affects up to 390 million[1] people around the world.

West Nile Virus: Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
West Nile virus is most commonly spread to humans when bitten by an infected mosquito. Learn about the symptoms of West Nile virus and how to help protect your loved ones from this mosquito-borne disease.

